Shockwave therapy and ultrasound therapy are two major modalities for pain-management in physiotherapy clinics to treat various musculoskeletal conditions such as chronic pain, tendonitis, and plantar fasciitis. Both treatments use energy waves to stimulate the healing process and reduce pain. However, there are distinctive differences between the two in terms of the type of energy wave used, the delivery method, the power output level, and the conditions that can be benefited from them. Therefore, comparing the two techniques can help determine which is appropriate for a specific condition to achieve optimal results.
What is ultrasound therapy?
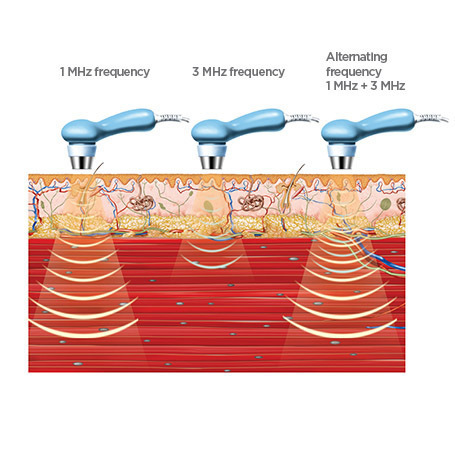
Ultrasound therapy was first introduced as a treatment for orthopedic conditions in the 1950s; the physiotherapist uses a therapeutic ultrasound device that outputs high-frequency sound waves, usually ranging from 0.75 to 3 MHz, with the aim of delivering energy to the affected area of the body.
What is shockwave therapy?
On the other hand, Shockwave Therapy has recently been widely recognized by healthcare providers. It generates high-energy sound waves to make rapid pressure changes that create a massage-like effect on the tissues.
Similarities of shockwave and ultrasound
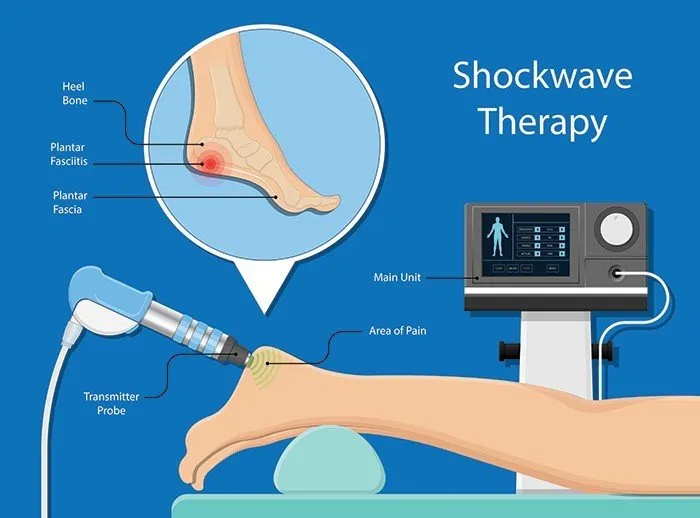
- Mechanically, both shockwave and ultrasound therapy utilize sound wave to transmit energy to the affected body area.
- They are both non-invasive treatments and are commonly used in physiotherapy and rehabilitation.
- Both ultrasound and shockwave therapy can help reduce pain, swelling, and muscle spasms. The energy waves they produce can also stimulate blood flow, promoting the healing process in certain orthopedic conditions.
What are the differences between ultrasound and shockwave?
- Even though both modalities use the sound wave to deliver energy, shockwave carries a broader range of frequencies from 1 to 22 kilohertz (KHz), which is relatively lower than ultrasound outputs of up to 3 megahertz (MHz). Since shockwave therapy employs lower-frequency sound wave, the energy can penetrate deeper into the tissues than ultrasound therapy, making it more effective for treating deeper-seated conditions.
- Shockwave therapy normally operates at higher energy levels than ultrasound therapy. In orthopedic practice, the PSI (Pounds per Square Inch) rate refers to the amount of pressure generated by the device. The energy developed by shockwave can range from 2 to 7 PSI, which is more elevated intensity and impact than ultrasound.
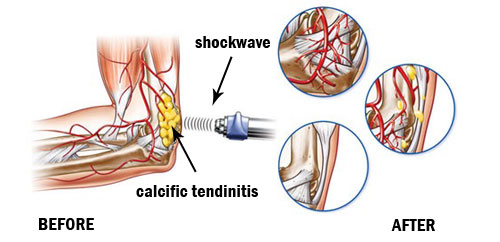
- Due to its higher energy output and deeper sound wave penetration, shockwave therapy can be effective for breaking up any calcifications or scar tissue that may be contributing to pain conditions such as plantar fasciitis, tennis elbow, rotator cuff, and other chronic musculoskeletal pain. In contrast, ultrasound therapy produces high-frequency sound waves that can create heat for better blood flow. Therefore, ultrasound has advantages in treating conditions such as tendinitis, bursitis, and joint pain caused by arthritis.
- Since shockwave usually produces higher intensity and pressure force on the affected area, the treatment might be uncomfortable or even painful to the patient with low pain tolerance levels, while ultrasound therapy is generally pain-free.
Choosing the right one
Thanks for its high energy performance and more intensive treatment. Recent studies show that shockwave therapy has higher success rates in certain conditions than ultrasound, such as tennis elbow, jumper’s knee, plantar fasciitis, rotator cuff and calcific tendinitis.
Even with handsful specifications that outperform the alternative, it needs to be more accurate to conclude that shockwave is superior to ultrasound in every way. Due to its high power and intensity, shockwave therapy is not recommended to treat fractures, osteoporosis and post-op conditions. Because it may weaken or even damage the already fragile bones. Furthermore, when treating joint pain from arthritis, the shockwave is not well suited as it may aggravate the underlying inflammation. For patients with low pain tolerance levels, ultrasound therapy is the preferable treatment with a longer duration.
Shockwave and ultrasound near me
Both shockwave and ultrasound therapy share some similarities, and they all have significant pros and cons, but the best choice depends on the specific condition and individual patient. Thus it is critical to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment. At Pro Fusion Rehab, all our registered physiotherapists have extensive knowledge and experience in implementing ultrasound and shockwave therapy; feel free to contact us before undergoing either ultrasound or shockwave therapy to determine if it is a safe and effective option for your orthopedic condition.
References:
Jia, L. (2016, October 17). Efficacy of focused low-intensity pulsed ultrasound therapy for the management of knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nature. https://www.nature.com/articles/srep35453?error=cookies_not_supported&code=704b37b9-99df-40a1-9537-e95cc14c0839
Dedes, V., Tzirogiannis, K., Polikandrioti, M., Dede, A., Nikolaidis, C., Mitseas, A., & Panoutsopoulos, G. (2019). Radial Extra Corporeal Shockwave Therapy Versus Ultrasound Therapy in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis. Acta Informatica Medica, 27(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.5455/aim.2019.27.45-49
Smallcomb, M., Khandare, S., Vidt, M. E., & Simon, J. C. (2021). Therapeutic Ultrasound and Shockwave Therapy for Tendinopathy. American Journal of Physical Medicine &Amp; Rehabilitation, 101(8), 801–807. https://doi.org/10.1097/phm.0000000000001894