Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide, especially in the older adults, it is the most common type of arthritis. As the protective cartilage in our joints wears down over time, the bones start to rub against each other, causing pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. This condition can significantly impact an individual’s ability to perform daily activities and enjoy a high quality of life.
While osteoarthritis is often associated with the natural aging process, it can also develop due to joint injuries, obesity, or genetic factors. Common joints affected by OA include the knees, hips, hands, and spine, making even simple tasks like walking, climbing stairs, or opening jars a challenge.
One of the most effective and non-invasive ways to manage osteoarthritis is through physiotherapy. it is a holistic treatment approach that focuses on restoring movement, reducing pain, and improving functional ability through a combination of exercises, manual therapy techniques, and education.
What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage – the smooth, protective tissue covering the ends of bones where they form a joint. As this cartilage deteriorates, the bones begin to rub against each other, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Common Causes:
- Age – OA is most common in older adults as cartilage wears down over time.
- Obesity – Excess weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints like knees and hips.
- Joint Injuries – Injuries from sports, accidents or repeated stress on a joint increase OA risk.
- Genetics – Some people inherit a greater likelihood of developing osteoarthritis.
Commonly Affected Joints:
- Knees
- Hips
- Hands
- Spine (neck and lower back)
Key Symptoms:
- Joint pain and tenderness, often worse with activity
- Stiffness after periods of rest or inactivity
- Swelling around affected joints
- Limited range of motion and flexibility
- Grating sensation when using the joint
- Bone spurs around the joint
As cartilage loss progresses, major weight-bearing joints like knees and hips become increasingly painful and difficult to move. Even simple daily tasks like walking, climbing stairs, or gripping objects can become challenging for those with advanced osteoarthritis. Managing symptoms through physiotherapy helps improve mobility and quality of life.
Physiotherapy interventions for osteoarthritis:
- Exercise Programs
- Exercise is a cornerstone of OA treatment. A physiotherapist will prescribe a tailored exercise program focusing on:
- Range of motion exercises to improve joint flexibility and mobility
- Strengthening exercises for the muscles supporting the affected joints to reduce stress
- Low-impact aerobic exercises like walking, cycling or swimming to improve cardiovascular health and assist with weight management
- Manual Therapy, Physiotherapists use their hands to apply specific techniques such as:
- Joint mobilizations and manipulations to improve joint mobility and range of motion
- Soft tissue massage to reduce muscle tension and spasms around joints
- Joint traction to relieve compression and stretch joint surfaces
- Modalities
- Various therapeutic modalities can be used as adjuncts:
- Heat/cold therapy to temporarily relieve pain and muscle spasms
- Therapeutic ultrasound to promote tissue healing
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) to interrupt pain signals
- Assistive Devices, Physiotherapists recommend and fit appropriate assistive aids:
- Braces/splints to support and stabilize affected joints
- Canes/Walkers to improve stability and reduce weight-bearing stress
- Orthotics/Specialized footwear to correct gait abnormalities
- Education and Self-Management, a major role is to educate patients on:
- Joint protection techniques to reduce excessive stress
- Proper body mechanics for daily activities
- Weight loss strategies if overweight
- Pain management strategies like pacing and relaxation
- Home exercise programs to continue prescribed exercises
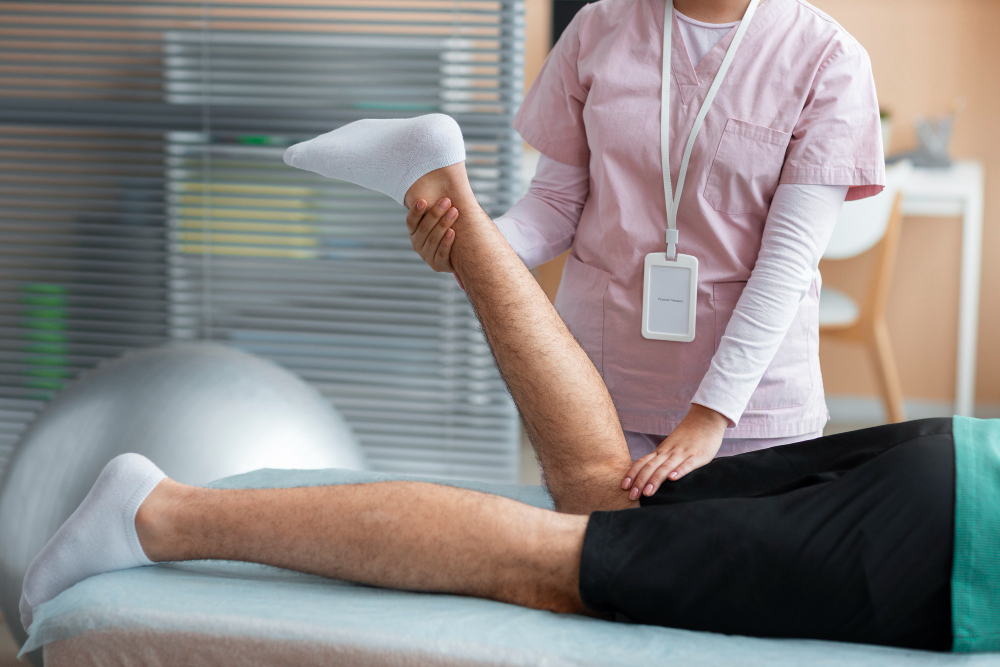

Physiotherapy offers a multitude of benefits for those living with osteoarthritis. Through personalized exercise programs, manual therapies, therapeutic modalities, and assistive devices, physiotherapists can effectively alleviate pain, restore mobility and flexibility, strengthen supporting muscles, and promote joint health.
Early intervention is key when it comes to osteoarthritis management. By seeking physiotherapy treatment promptly after experiencing symptoms or receiving a diagnosis, you can halt or slow the progression of joint damage. Consistent treatment and adherence to the prescribed exercise and self-care regimen are essential for achieving optimal results and long-term benefits.
Find the physiotherapist near you
If you or a loved one is struggling with the challenges of osteoarthritis, it is highly recommended to consult with a licensed physiotherapist. At Pro Fusion Rehab, our physiotherapists in Pickering and Milton clinic are specialized health professionals will conduct a thorough evaluation and develop a customized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs, affected joints, and lifestyle goals.
References:
Khan, S. A., Parasher, P., Ansari, M. A., Parvez, S., Fatima, N., & Alam, I. (2023, February 14). Effect of an integrated physiotherapy protocol on KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS PATIENTS: A preliminary study. Healthcare (Basel, Switzerland). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9956031/
WebMD. (n.d.). Exercises for knee osteoarthritis and joint pain. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/osteoarthritis/ss/slideshow-knee-exercises
