What is Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy describes the use of electrical current to create an stimulative effect in the body. Physiotherapists use electrical currents at low levels to reduce the sensation of pain. It may work either by “scrambling” pain signals to mask feelings of pain or by causing the body to produce natural pain-killers called endorphins.
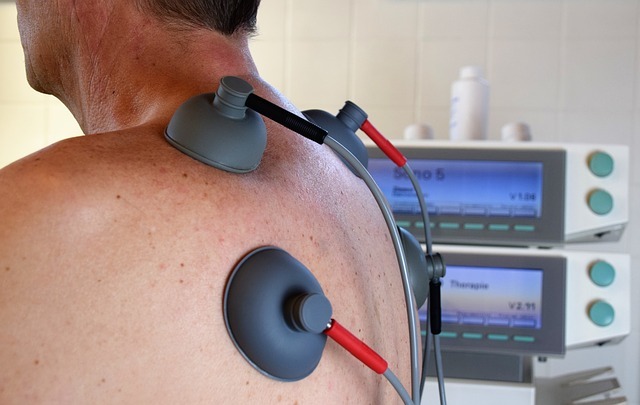
How Electrotherapy helps to reduce pain?
Physiotherapists can use electrical stimulation to cause muscles to tense to help the maintenance of muscle tone when muscles would otherwise lose strength or help retrain muscles to contract again.
Examples of Electrotherapy treatment include:
- Recovery from Stroke.
- Pain management for Arthritis.
- Rehabilitation from Surgery.
- Maintain tone in the shoulder muscles to better hold the joint together for pain management.
- Upkeeping leg strength in severe arthritis of the knee to remedy pain during exercise.
- Stimulate muscles at the front of the thigh to encourage proper functional order after knee surgery.
Benefits of Electrotherapy
The benefits of electrotherapy are wide-ranging and include a more advanced healing process, a more effective circulatory system, and increased muscle tone. Electrotherapy will ultimately increase muscle tone, range of movement, speed and strength of muscle contractions, and an increased rate of absorption.
- Increasing blood flow to the injured area, which promotes healing.
- Reducing inflammation.
- Decrease in pain.
- Break down of scar tissue and adhesions.
Conditions and types of pain can benefit from Electrotherapy treatment
- Acute and chronic ankle pain and ankle joint arthritis.
- Acute and chronic low back pain.
- Spinal nerve and disc pain or spinal osteoarthritis/degenerative disc disease(DDD).
- Acute and chronic neck pain associated with soft tissue injury.
- Joint inflammation and spinal arthritis.
- Acute, chronic and post surgical knee pain.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Foot pain including Plantar Fasciitis and Achilles Tendinopathy.
- TMJ pain(jaw joint).
- Hip pain.
- Sciatica.
- Bicipital tendonitis.
- Tennis elbow.
- Wrist pain.
- Fibromyalgia.
- Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD).